https://github.com/returu/CityQuantHub项目概述
https://lbs.amap.com/api/webservice/guide/api-advanced/search-
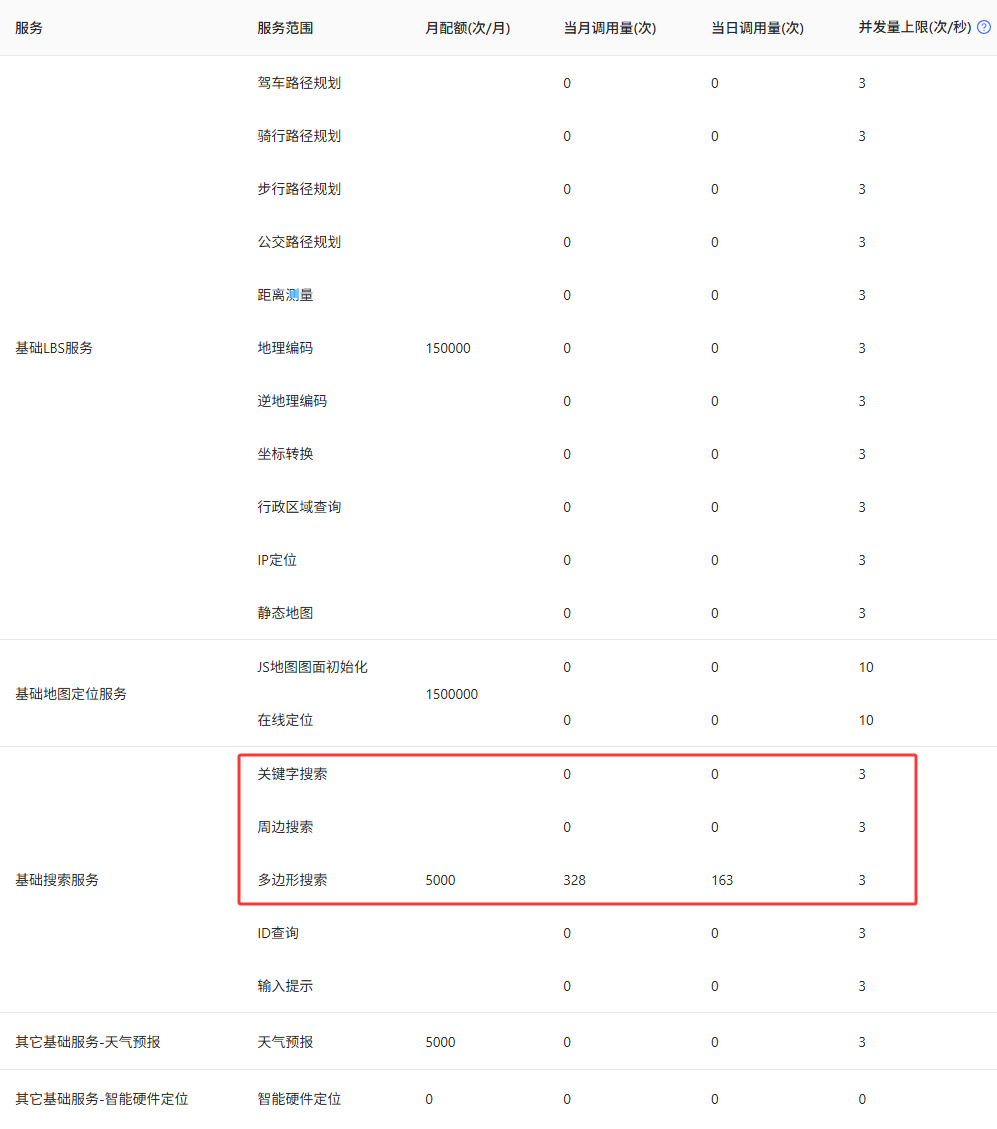
一个key一个月只有5000次的免费配额; -
一次请求只能获取200个POI数据。
-
通过高德行政区域查询API获取行政区边界的外接矩形范围,将其划分为多个小网格。然后只对与行政区相交的小网格请求POI数据,避免请求数据量过大; -
设置多个key,通过自动切换 API Key 以避免额度限制; -
每次尽量使用POI类型代码中的小类,例如餐饮服务(大类)→快餐厅(中类)→肯德基(小类)。
https://lbs.amap.com/https://lbs.amap.com/api/webservice/download代码解析
-
获取城市边界坐标:通过高德地图的区域查询 API,根据城市编码获取目标城市的边界坐标数据。 -
网格划分:将城市边界范围划分为多个小网格,这样做的目的是为了避免一次性请求过大范围导致的 API 限制。 -
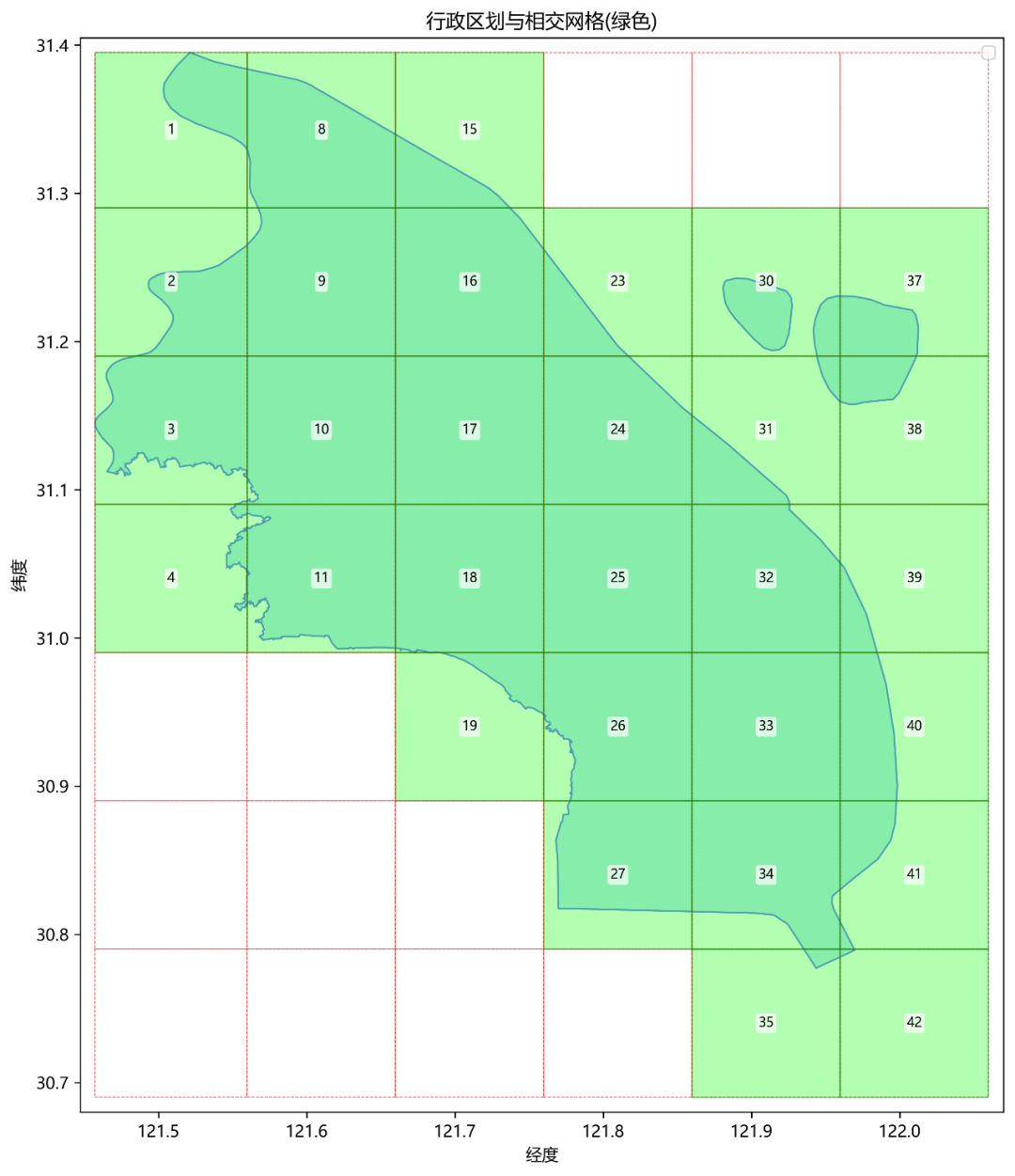
筛选有效网格:可视化展示网格与城市边界的相交情况,筛选出真正位于城市范围内的网格,减少API访问量(如下图所示)。 -
POI 数据获取:针对每个有效网格,使用多边形搜索 API 获取其中的 POI 数据,并将经纬度坐标从火星坐标系转换为WGS84坐标系。 -
数据存储:将获取到的 POI 数据保存到 CSV 文件中,方便后续分析使用。
程序主要由四个核心类组成:CityCoordinateExtractor、ProcessAndVisualizeGrids、CoordinateConverter和 GaodePoi。如需使用的话,在主程序的参数设置部分根据需要设置几个必须参数即可。
程序所需模块如下,其中需要手动安装的第三方库包括pandas、geopandas、shapely 和 matplotlib,其中,geopandas安装需要许多依赖包,具体安装可以查看以下文章:
【GeoPandas空间数据分析】1.GeoPandas简介
import math
import json
import csv
import time, os
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
from urllib import request
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, Point, MultiPolygon
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
1、CityCoordinateExtractor类:获取城市边界坐标的矩形范围
,为后续的网格划分和POI数据获取奠定基础。该类包含以下三个方法:-
switch_key方法:当当前使用的key因请求过多等原因失效时,切换到下一个key。 -
log_message方法:用于记录日志信息,如果提供了日志回调函数,则调用该函数记录日志,否则直接打印到控制台。 -
get_coords方法:这是核心方法,通过调用高德地图的行政区查询API,获取城市边界坐标及其对应的矩形范围。
需要注意的是,当一个行政区范围由完全分隔两块或者多块的地块组成时,高德API返回的每块地的 polyline 坐标串会以 | 分隔 。因此在代码中需要检查是否包含多个地块,以便采取不同的数据处理方式。
# ============== 城市坐标提取类 ==============
# ======== 获取城市边界坐标的矩形范围 ========
class CityCoordinateExtractor(object):
def __init__(self, key_list, citycode, log_callback=None):
"""
初始化城市坐标提取器
:param key_list: 高德API密钥列表,用于轮换请求
:param citycode: 目标城市编码(如上海浦东新区为310115)
:param log_callback: 日志回调函数,默认为print
"""
self.key_list = key_list # key列表
self.citycode = citycode # 城市编码
self.current_key_index = 0 # 当前使用的key索引
self.current_key = key_list[0] if key_list else None # 当前使用的key
self.log_callback = log_callback if log_callback elseprint# 日志记录函数
def switch_key(self):
"""切换到下一个API密钥,用于应对请求限制或密钥失效"""
if not self.key_list:
raise ValueError("没有可用的key")
# 更新密钥索引(循环轮换)
self.current_key_index = (self.current_key_index + 1) % len(self.key_list)
self.current_key = self.key_list[self.current_key_index]
self.log_message(f"已切换到备用key: {self.current_key[:5]}...")
time.sleep(2) # 切换key后等待2秒,避免立即请求失败
def log_message(self, message):
"""记录日志信息,支持自定义日志函数"""
if self.log_callback:
self.log_callback(message)
else:
print(message)
def get_coords(self):
"""
获取城市边界坐标及矩形范围(bbox)
:return: (行政区划坐标字符串, 矩形范围字符串),失败时返回(0, None)
"""
max_attempts = len(self.key_list) # 最大尝试次数(等于密钥数量)
for attempt in range(max_attempts):
try:
# 构造高德API请求URL,获取行政区划数据
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/config/district?key={self.current_key}&keywords={self.citycode}&extensions=all'
response = request.urlopen(url)
json_result = json.load(response)
# 提取行政区划坐标字符串(polyline格式)
polyline_coordinates = json_result["districts"][0]["polyline"]
# 初始化经纬度极值(用于计算bbox)
min_longitude = float('inf')
max_longitude = float('-inf')
min_latitude = float('inf')
max_latitude = float('-inf')
# 处理多地块情况(坐标用"|"分隔)
if"|"in polyline_coordinates:
polygons = polyline_coordinates.split("|")
else:
polygons = [polyline_coordinates] # 单个地块
# 遍历每个地块的坐标点,计算经纬度极值
for polygon in polygons:
# 将字符串分割成坐标对
coordinates_list = polygon.split(";")
# 遍历每个坐标对
for coord in coordinates_list:
if coord.strip(): # 确保坐标对不为空(使用strip()去除可能的空白字符)
try:
longitude, latitude = map(float, coord.split(","))
# 更新经纬度最大和最小值
min_longitude = min(min_longitude, longitude)
max_longitude = max(max_longitude, longitude)
min_latitude = min(min_latitude, latitude)
max_latitude = max(max_latitude, latitude)
except ValueError as e:
self.log_message(f"坐标解析错误: {coord} - {str(e)}")
continue
# 检查是否获取到有效坐标
if (min_longitude == float('inf') or max_longitude == float('-inf') or
min_latitude == float('inf') or max_latitude == float('-inf')):
raise ValueError("未能解析到有效的坐标数据")
# 构造bbox字符串(格式:左上|右下,即min_lng,max_lat|max_lng,min_lat)
bbox_str = f"{min_longitude},{max_latitude}|{max_longitude},{min_latitude}"
return polyline_coordinates, bbox_str
except Exception as e:
self.log_message(f"请求异常: {str(e)}")
if attempt < max_attempts - 1:
self.switch_key() # 尝试切换密钥
else:
self.log_message("所有key都已尝试,仍然失败")
return 0, None
return 0, None
-
2、ProcessAndVisualizeGrids类:处理网格划分和可视化
-
divide_latitude方法:将纬度范围按照指定的网格大小进行划分,从北向南(纬度递减)划分网格直到覆盖整个区域。 -
divide_longitude方法:将经度范围按照指定的网格大小进行划分,从西向东(经度递增)划分网格直到覆盖整个区域。 -
generate_grid_coordinates方法:组合经纬度划分结果,生成所有小网格的坐标对,格式为”左上经度,左上纬度|右下经度,右下纬度”。 -
visualize_grids方法:这是该类的核心方法之一,用于将城市边界与划分出的网格一同可视化展示出来。在图形中,与城市边界相交的网格会被突出显示,并标注上网格编号。最后,将绘制好的图形保存为图片文件,并返回与城市边界相交的网格的坐标列表。
# ============== 网格划分与可视化类 ==============
class ProcessAndVisualizeGrids(object):
def __init__(self, coordinates , bbox_str, grid_size):
"""
初始化网格处理与可视化工具
:param coordinates: 行政区划原始坐标数据(polyline格式)
:param bbox_str: 矩形范围字符串(用于构建API请求参数)
:param grid_size: 网格划分的度数大小(如0.1度)
"""
self.bbox_str = bbox_str
self.grid_size = grid_size
self.coordinates = coordinates
def divide_latitude(self):
"""
划分纬度方向的网格线
:return: 纬度坐标列表(从最大值开始,按grid_size递减)
"""
lat_max = float(self.bbox_str.split('|')[0].split(',')[1]) # 提取bbox中的最大纬度
lat_min = float(self.bbox_str.split('|')[1].split(',')[1]) # 提取bbox中的最小纬度
lat_list = [str(lat_max)]
# 按grid_size递减生成纬度线
while lat_max - lat_min > 0:
m = lat_max - self.grid_size
lat_max = lat_max - self.grid_size
lat_list.append("{:.2f}".format(m))
return lat_list
def divide_longitude(self):
"""
划分经度方向的网格线
:return: 经度坐标列表(从最小值开始,按grid_size递增,排序后返回)
"""
lng_max = float(self.bbox_str.split('|')[1].split(',')[0]) # 提取bbox中的最大经度
lng_min = float(self.bbox_str.split('|')[0].split(',')[0]) # 提取bbox中的最小经度
lng_list = [str(lng_min)]
# 按grid_size递增生成经度线
while lng_max - lng_min > 0:
m = lng_min + self.grid_size
lng_min = lng_min + self.grid_size
lng_list.append("{:.2f}".format(m))
return sorted(lng_list) # 确保经度按升序排列
def generate_grid_coordinates(self):
"""生成所有网格的坐标范围(左上|右下)
:return: 网格坐标列表,每个元素为"nw_lng,nw_lat|se_lng,se_lat"格式
"""
lat = self.divide_latitude()
lng = self.divide_longitude()
ls = []
# 遍历经纬度网格线,生成每个网格的坐标范围
for i in range(len(lng)-1):
for j in range(len(lat)-1):
# 左上角(西北)坐标
northwest = f"{lng[i]},{lat[j]}"
# 右下角(东南)坐标
southeast = f"{lng[i+1]},{lat[j+1]}"
coor = northwest + '|' + southeast
ls.append(coor)
return ls
def visualize_grids(self):
"""
可视化行政区划与网格的相交情况,并返回与行政区划相交的网格坐标
:return: 相交网格的坐标列表(格式同generate_grid_coordinates)
"""
# 处理坐标数据 - 修改为处理多个多边形的情况
polygons = []
for poly_coords in self.coordinates.split('|'):
points = [tuple(map(float, point.split(','))) for point in poly_coords.split(';')]
polygons.append(Polygon(points))
# 创建行政区划几何对象(单个或多个多边形)
if len(polygons) == 1:
admin_geometry = polygons[0]
else:
admin_geometry = MultiPolygon(polygons)
# 创建行政区划GeoDataFrame
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(index=[0], geometry=[admin_geometry])
# 创建网格
grid_cells = self.generate_grid_coordinates()
# 准备网格数据(用于GeoDataFrame)
grid_data = []
for idx, cell in enumerate(grid_cells, start=1):
nw, se = cell.split('|')
nw_lng, nw_lat = map(float, nw.split(','))
se_lng, se_lat = map(float, se.split(','))
# 创建网格多边形
grid_polygon = Polygon([
(nw_lng, nw_lat),
(se_lng, nw_lat),
(se_lng, se_lat),
(nw_lng, se_lat)
])
# 计算网格中心点
center_lng = (nw_lng + se_lng) / 2
center_lat = (nw_lat + se_lat) / 2
center_point = Point(center_lng, center_lat)
grid_data.append({
'id': idx,
'geometry': grid_polygon,
'center': center_point,
'nw': (nw_lng, nw_lat),
'se': (se_lng, se_lat)
})
# 创建网格GeoDataFrame
grid_gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(grid_data)
# 找出与行政区划相交的网格
intersected_grids = grid_gdf[grid_gdf.intersects(admin_geometry)].copy()
# 绘制地图
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 10))
# 绘制行政区划(浅蓝色背景,蓝色边框)
gdf.plot(ax=ax, color='skyblue', edgecolor='blue', alpha=0.5, label='行政区划')
# 绘制所有网格(红色虚线边框)
for _, row in grid_gdf.iterrows():
rect = plt.Rectangle(
(row['nw'][0], row['se'][1]),
row['se'][0] - row['nw'][0],
row['nw'][1] - row['se'][1],
fill=False,
edgecolor='red',
linewidth=0.5,
linestyle='--',
alpha=0.7
)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 突出显示相交网格(绿色填充,绿色边框)
for _, row in intersected_grids.iterrows():
rect = plt.Rectangle(
(row['nw'][0], row['se'][1]),
row['se'][0] - row['nw'][0],
row['nw'][1] - row['se'][1],
fill=True,
edgecolor='green',
facecolor='lime',
linewidth=1,
alpha=0.3
)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 添加网格编号(白色背景框)
ax.text(
row['center'].x, row['center'].y,
str(row['id']),
ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=8,
color='black',
bbox=dict(
boxstyle='round,pad=0.2',
fc='white',
ec='none',
alpha=0.7
)
)
# 设置图形属性
ax.set_title('行政区划与相交网格(绿色)')
ax.set_xlabel('经度')
ax.set_ylabel('纬度')
ax.grid(False)
ax.legend()
# 设置坐标轴范围(略大于网格范围,避免边框被截断)
min_x = min([row['nw'][0] for _, row in grid_gdf.iterrows()]) - 0.01
max_x = max([row['se'][0] for _, row in grid_gdf.iterrows()]) + 0.01
min_y = min([row['se'][1] for _, row in grid_gdf.iterrows()]) - 0.01
max_y = max([row['nw'][1] for _, row in grid_gdf.iterrows()]) + 0.01
ax.set_xlim(min_x, max_x)
ax.set_ylim(min_y, max_y)
plt.tight_layout()
# 保存图片
plt.savefig("./行政区划与相交网格(绿色).png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# 获取相交网格的编号和对应的坐标
selected_ids = intersected_grids['id'].tolist()
intersected_grid_cells = [grid_cells[i-1] for i in selected_ids]
# 返回相交网格的左上角(西北)坐标和右下角(东南)
return intersected_grid_cells
-
3、CoordinateConverter类:坐标转换
# ================== 坐标转换类 ==================
# ======== GCJ02(火星坐标系)转WGS84坐标系 ========
class CoordinateConverter(object):
def __init__(self):
self.x_pi = 3.14159265358979324 * 3000.0 / 180.0
self.pi = 3.1415926535897932384626 # π
self.a = 6378245.0 # 长半轴
self.ee = 0.00669342162296594323 # 偏心率平方
def gcj02_to_wgs84(self, lng, lat):
"""
GCJ02(火星坐标系)转GPS84(世界标准坐标系)
参数:
lng: 经度(GCJ02)
lat: 纬度(GCJ02)
返回:
list: [经度(WGS84), 纬度(WGS84)]
"""
# 计算偏移量
dlat = self._transformlat(lng - 105.0, lat - 35.0)
dlng = self._transformlng(lng - 105.0, lat - 35.0)
# 坐标转换的数学计算
radlat = lat / 180.0 * self.pi
magic = math.sin(radlat)
magic = 1 - self.ee * magic * magic
sqrtmagic = math.sqrt(magic)
# 计算偏移修正量
dlat = (dlat * 180.0) / ((self.a * (1 - self.ee)) / (magic * sqrtmagic) * self.pi)
dlng = (dlng * 180.0) / (self.a / sqrtmagic * math.cos(radlat) * self.pi)
mglat = lat + dlat
mglng = lng + dlng
# 利用反向计算获取WGS-84坐标(通过对称原理)
return [lng * 2 - mglng, lat * 2 - mglat]
def _transformlat(self, lng, lat):
"""
纬度转换辅助函数 - 计算纬度偏移量
使用多项式和三角函数组合的经验公式
"""
ret = -100.0 + 2.0 * lng + 3.0 * lat + 0.2 * lat * lat +
0.1 * lng * lat + 0.2 * math.sqrt(math.fabs(lng))
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(6.0 * lng * self.pi) + 20.0 *
math.sin(2.0 * lng * self.pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(lat * self.pi) + 40.0 *
math.sin(lat / 3.0 * self.pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (160.0 * math.sin(lat / 12.0 * self.pi) + 320 *
math.sin(lat * self.pi / 30.0)) * 2.0 / 3.0
return ret
def _transformlng(self, lng, lat):
"""
经度转换辅助函数 - 计算经度偏移量
使用多项式和三角函数组合的经验公式
"""
ret = 300.0 + lng + 2.0 * lat + 0.1 * lng * lng +
0.1 * lng * lat + 0.1 * math.sqrt(math.fabs(lng))
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(6.0 * lng * self.pi) + 20.0 *
math.sin(2.0 * lng * self.pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(lng * self.pi) + 40.0 *
math.sin(lng / 3.0 * self.pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (150.0 * math.sin(lng / 12.0 * self.pi) + 300.0 *
math.sin(lng / 30.0 * self.pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0
return ret
-
4、GaodePoi类:API 请求与数据处理
该类的主要作用是根据指定的POI类型编码和网格坐标,通过高德地图API逐个网格地获取到所需的POI数据,并将它们以字典的形式输出,为后续的数据存储和分析提供了便利。该类包含以下方法:
-
switch_key方法:当当前使用的key因请求过多等原因失效时,切换到下一个key,并在切换后等待2秒,避免立即请求失败。 -
log_message方法:用于记录日志信息,如果提供了日志回调函数,则调用该函数记录日志,否则直接打印到控制台。 -
get_count方法:这是核心方法之一,通过调用高德地图的POI查询API,获取指定网格内POI的总数,并返回有效count(POI数量信息)和key。 -
getPOIs方法:根据获取到的有效count和key,分页请求网格内的POI数据。对于获取到的每一个POI,会提取其关键信息,如ID、经纬度、名称、类型、地址等,并将这些数据以字典的形式逐条输出。
# ============== POI数据获取类 ==============
class GaodePoi(object):
def __init__(self, type_code, polygon, key_list, filename, log_callback=None):
"""
初始化POI数据获取器
:param type_code: POI类型编码(如050301表示肯德基)
:param polygon: 搜索区域多边形坐标(格式:nw_lng,nw_lat|se_lng,se_lat)
:param key_list: 高德API密钥列表
:param filename: 保存POI数据的文件名
:param log_callback: 日志回调函数
"""
self.type_code = type_code
self.polygon = polygon
self.key_list = key_list
self.current_key_index = 0
self.filename = filename
self.current_key = key_list[0] if key_list else None
self.log_callback = log_callback if log_callback elseprint
self.converter = CoordinateConverter() # 初始化坐标转换器
def switch_key(self):
"""切换API密钥,逻辑同CityCoordinateExtractor"""
if not self.key_list:
raise ValueError("没有可用的key")
self.current_key_index = (self.current_key_index + 1) % len(self.key_list)
self.current_key = self.key_list[self.current_key_index]
print(f"已切换到备用key: {self.current_key[:5]}...")
time.sleep(2) # 切换key后等待2秒,避免立即请求失败
def log_message(self, message):
"""记录日志信息,逻辑同CityCoordinateExtractor"""
if self.log_callback:
self.log_callback(message)
else:
print(message)
def get_count(self):
"""
获取指定区域内的POI数量,并验证密钥有效性
:return: (POI数量, 有效密钥),失败时返回(0, None)
"""
max_attempts = len(self.key_list)
for attempt in range(max_attempts):
try:
# 构造请求URL(获取POI数量)
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/place/polygon?key={self.current_key}&types={self.type_code}&polygon={self.polygon}&offset=20&page=1&extensions=all'
response = request.urlopen(url)
poi_json = json.load(response)
# 检查API返回状态,处理API错误
if poi_json['status'] == '0':
if poi_json['info'] in ('INVALID_USER_KEY', 'DAILY_QUERY_OVER_LIMIT'):
print(f"Key失效: {self.current_key[:5]}..., 错误信息: {poi_json['info']}")
self.switch_key()
continue
else:
print(f"API请求错误: {poi_json['info']}")
return 0, None
count = int(poi_json['count'])
print(f"当前使用key: {self.current_key[:5]}..., 状态: {poi_json['status']}, 找到 {count} 个POI")
time.sleep(1)
return count, self.current_key # 返回有效count和key
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求异常: {str(e)}")
if attempt < max_attempts - 1:
self.switch_key()
else:
print("所有key都已尝试,仍然失败")
return 0, None
return 0, None
def getPOIs(self):
"""
分页获取POI数据并生成器返回
:yield: 每个POI的字典数据(包含id、经纬度、名称等信息)
"""
count, valid_key = self.get_count()
if count == 0 or not valid_key:
print("无数据或无有效key......")
return
# 计算总页数(每页20条)
pages = count // 20 + 1
for page in range(1, pages+1):
try:
print(f'使用有效key: {valid_key[:5]}..., 正在获取第 {page}/{pages} 页数据')
# 构造分页请求URL
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/place/polygon?key={valid_key}&types={self.type_code}&polygon={self.polygon}&offset=20&page={page}&extensions=all'
response = request.urlopen(url)
poi_json = json.load(response)
# 检查API返回状态
if poi_json['status'] == '0':
# 理论上这里不会出现key失效的情况,因为使用的是已经验证过的有效key
print(f"API请求错误: {poi_json['info']}")
break
pois = poi_json['pois']
for poi in pois:
result = {}
result["poi_id"] = poi['id']
# 获取原始坐标并转换为WGS84
lon_gcj02 = float(poi['location'].split(',')[0]) # 经度(GCJ02)
lat_gcj02 = float(poi['location'].split(',')[1]) # 纬度(GCJ02)
lon_wgs84, lat_wgs84 = self.converter.gcj02_to_wgs84(lon_gcj02, lat_gcj02)
result["lon"] = lon_wgs84 # 经度(WGS84)
result["lat"] = lat_wgs84 # 纬度(WGS84)
result["name"] = poi['name']
result["poi_type"] = poi['type']
result["poi_type_code"] = poi['typecode']
result["cityname"] = poi['cityname']
result["adname"] = poi['adname']
result["address"] = poi['address']
yield result
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求异常: {str(e)}")
time.sleep(3)
-
4、主程序流程:整合上述功能,实现完整流程
在主程序的参数设置部分需要设置以下几个必须参数:
-
key_list:API密钥列表,需要替换为实际可用的密钥; -
type_code:指定POI类型编码,尽量使用POI类型代码中的小类以避免单次请求的数量限制; -
citycode:指定城市行政区编码;
-
grid_size:网格大小(单位为度),需合理设置网格大小,太小会导致API调用次数剧增; -
filename:结果文件名,也可不设置,程序会自动以POIs_<POI类型编码>名称保存。
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""
参数设置部分
"""
key_list = [
'a0fb96ac90b99497e519e3f811ca7e98', # 请替换为实际的备用key
'key2', # 请替换为实际的备用key
'key3', # 请替换为实际的备用key
]
type_code = '050301'# POI类型编码(示例:050301表示肯德基)
citycode = 310115 # 城市编码(示例:310115表示上海市浦东新区)
filename = f'POIs_{type_code}.csv'# 保存POI数据的文件名
grid_size = 0.1 # 网格大小(度),用于划分搜索区域
"""
数据爬取主流程
"""
# 1. 提取城市边界坐标及矩形范围
extractor = CityCoordinateExtractor(key_list,citycode)
polyline_coordinates , bbox_str = extractor.get_coords()
if not polyline_coordinates or not bbox_str:
print("获取城市坐标失败,程序终止")
exit()
# 2. 划分网格并可视化相交区域
grids = ProcessAndVisualizeGrids(polyline_coordinates , bbox_str, grid_size)
intersected_grid_cells = grids.visualize_grids()
print(f"共找到 {len(intersected_grid_cells)} 个与行政区划相交的网格")
# 3. 检查文件是否存在(用于追加写入时判断是否需要写入表头)
file_exists = os.path.isfile(filename)
# 4. 遍历相交网格,获取POI数据
poi_num = 0
num_grids = len(intersected_grid_cells)
for loc in intersected_grid_cells:
print(f"剩余网格数:{num_grids}")
num_grids -= 1
# 初始化POI获取器(每个网格独立请求)
par = GaodePoi(type_code=type_code, polygon=loc, key_list=key_list, filename=filename)
# 获取当前网格的POI数量,忽略返回的key(使用内部验证的有效key)
count, _ = par.get_count()
poi_num += count
print(f"本次共获取{count}个poi数据")
print(f"总共获取{poi_num}个poi数据")
# 分页获取POI数据并保存
dt = par.getPOIs()
df = pd.DataFrame(dt)
if len(df) != 0:
# 追加写入CSV文件(首次写入时包含表头)
df.to_csv(filename, header=not file_exists, index=False, encoding='utf_8_sig', mode='a+')
file_exists = True # 标记文件已存在,后续写入不再包含表头
time.sleep(1)
else:
pass注意事项:使用API时请遵守高德地图的使用条款,以免被封禁IP。


本篇文章来源于微信公众号: 码农设计师
