本系列文章配套代码获取有以下两种途径:
-
通过百度网盘获取:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jG-rGG4QMuZu0t0kEEl7SA?pwd=mnsj提取码:mnsj
-
前往GitHub获取:
https://github.com/returu/Data_Visualization函数语法:
plt.plot(*args, scalex=True, scaley=True, data=None, **kwargs)-
*args:
plt.plot(x, y, fmt)fmt (可选):格式字符串,用于快速指定线条样式、颜色和标记点,格式为 '[color][marker][line]'。例如:'ro-'表示红色(r)、圆圈标记(o)、实线(-)。'--g*'表示绿色(g)、星号标记(*)、虚线(--)。如果省略 fmt,默认使用实线('-')且无标记点。
-
scalex, scaley:
是否自动调整横轴(scalex)或纵轴(scaley)的显示范围。设为 False 时,Matplotlib 不会自动缩放对应轴的范围。默认为True。
-
data (可选):
-
**kwargs关键字参数:
**kwargs允许更精细地控制线条样式,常用的参数包括:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
plt.plot(
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[1, 4, 9, 16],
color='red', # 红色线条
linestyle='--', # 虚线
linewidth=2, # 线宽 2px
marker='o', # 圆圈标记
markersize=8, # 标记大小 8px
markerfacecolor='blue', # 标记填充蓝色
markeredgecolor='black', # 标记边缘黑色
label='示例曲线' # 图例标签
)
plt.legend()
plt.show()可视化结果如下图所示:
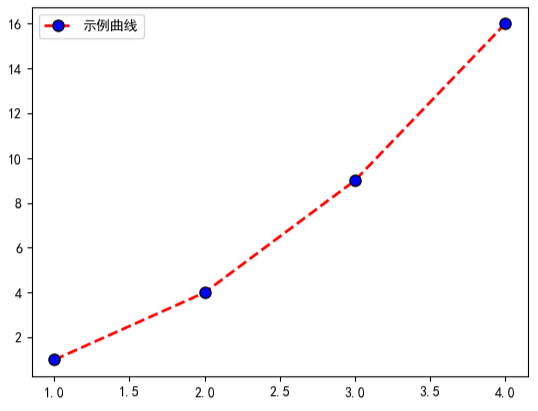
使用示例:
-
示例1:图表优化
-
突出关键数据点,例如对最高 / 最低温度等关键数据点进行特殊标记,增强视觉焦点;
-
添加平均水平线;
-
优化数据标签样式,让数据标签更精致,例如添加背景框避免与网格线重叠;
-
美化图表边框和刻度,例如调整边框显示和刻度样式,提升整体精致度;
-
添加数据来源标注。
# 准备数据
days = ['周一', '周二', '周三', '周四', '周五', '周六', '周日']
temp = [22, 24, 21, 25, 27, 26, 23]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# 绘制折线(设置线宽和标记样式)
plt.plot(
days, temp,
color='#E63946', linestyle='-', linewidth=2,
marker='o', markersize=8, markerfacecolor='white',
label='气温(℃)'
)
# 添加数据标签
for x, y in zip(days, temp):
# 在每个数据点上方添加数值标签
plt.text(
x, y + 0.8, # 标签位置(x坐标,y坐标+0.5避免与标记重叠)
f'{y}℃', # 标签内容
ha='center', # 水平居中对齐
va='bottom', # 垂直底部对齐
fontsize=10, # 字体大小
color='#333333', # 标签颜色
bbox=dict(facecolor='white', edgecolor='gray', pad=2, boxstyle='round,pad=0.5') # 添加背景框
)
# 找到最高和最低温度的位置,并进行特殊标记
max_idx = temp.index(max(temp))
min_idx = temp.index(min(temp))
plt.scatter(
days[max_idx], temp[max_idx],
color='#FF5733', s=100, edgecolor='black', zorder=5,
label=f'最高温 {temp[max_idx]}℃'
)
plt.scatter(
days[min_idx], temp[min_idx],
color='#33FFCE', s=100, edgecolor='black', zorder=5,
label=f'最低温 {temp[min_idx]}℃'
)
# 添加平均值参考线
avg_temp = sum(temp) / len(temp)
plt.axhline(
y=avg_temp, color='#555555', linestyle='--', linewidth=1.5,
label=f'平均气温 {avg_temp:.1f}℃'
)
# 添加图表细节
plt.title('某城市一周气温变化分析', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold', pad=20) # 标题加粗
plt.xlabel('星期', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
plt.ylabel('气温(℃)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
plt.ylim(15, 30) # 设置y轴范围
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3, linestyle=':') # 添加网格(透明度0.3,点线)
plt.legend(loc='lower right', fontsize=11) # 图例放在左下角
# 获取当前坐标轴对象
ax = plt.gca()
# 添加数据来源标注
plt.text(
0.02, 0.02, '数据来源:某城市气象局',
transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=9,
style='italic', color='gray'
)
# 调整背景色
ax.set_facecolor('#F8F9FA')
# 只显示底部和左侧边框,并加粗
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(1.5)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(1.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
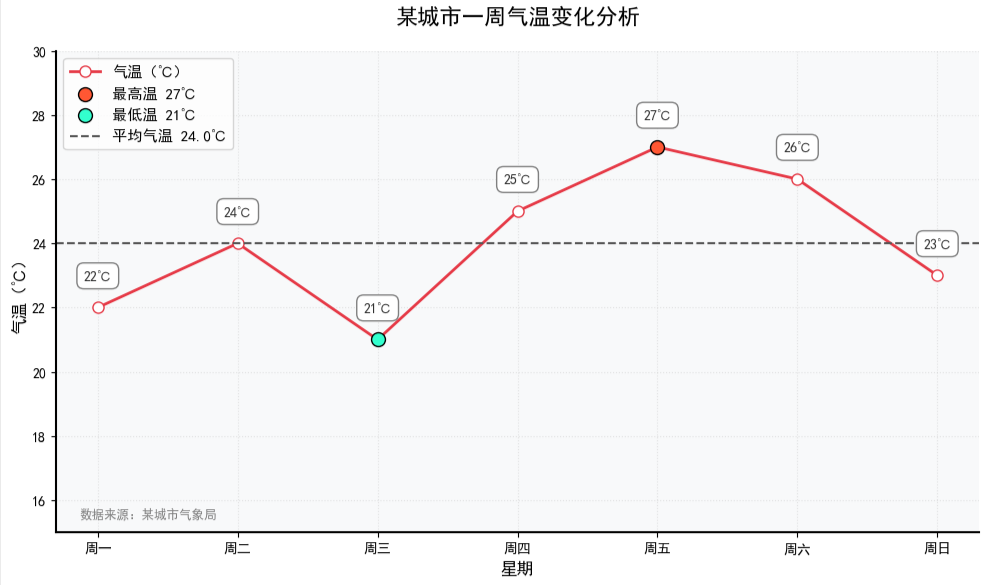
-
示例2:多条折线绘制
在 Matplotlib 中绘制多条折线有多种方法,核心思路是通过多次调用 plt.plot() 函数或一次性传入多组数据,
-
方法 1:多次调用 plt.plot()(最常用)
当折线数量较多时,可将数据和样式存入列表,通过循环批量绘制,减少重复代码。
# 准备数据
days = ['周一', '周二', '周三', '周四', '周五', '周六', '周日']
temp_high = [22, 24, 21, 25, 27, 26, 23] # 最高气温
temp_low = [15, 16, 14, 17, 18, 19, 16] # 最低气温
temp_avg = [18.5, 20, 17.5, 21, 22.5, 22.5, 19.5] # 平均气温
# 数据与样式打包
data = [
(temp_high, '#E63946', '-', 'o', '最高气温'),
(temp_low, '#06D6A0', '--', 's', '最低气温'),
(temp_avg, '#1D3557', '-.', '^', '平均气温')
]
# 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# 循环绘制
for y, color, ls, marker, label in data:
plt.plot(days, y, color=color, linestyle=ls, marker=marker, label=label)
# 添加图表元素
plt.title('某城市一周气温变化(最高/最低/平均)', fontsize=15, pad=20)
plt.xlabel('星期', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('气温(℃)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylim(10, 30) # 调整y轴范围
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.legend(
loc='best', # 位置自动
fontsize=11, # 字体大小
frameon=True, # 显示边框
fancybox=True, # 圆角边框
shadow=True, # 阴影效果
)
# 美化边框
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
可视化结果如下图所示:
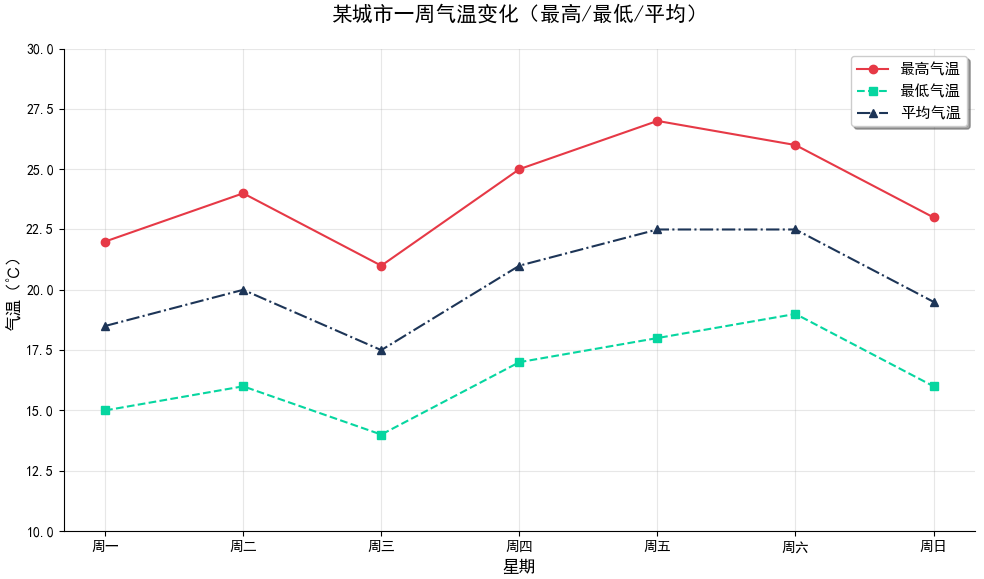
-
方法 2:一次性传入多组数据(简洁写法)
在单个 plt.plot() 中按 (x1, y1, 样式1, x2, y2, 样式2, ...) 的格式传入多组数据,适合快速绘图。
# 准备数据
days = ['周一', '周二', '周三', '周四', '周五', '周六', '周日']
temp_high = [22, 24, 21, 25, 27, 26, 23] # 最高气温
temp_low = [15, 16, 14, 17, 18, 19, 16] # 最低气温
temp_avg = [18.5, 20, 17.5, 21, 22.5, 22.5, 19.5] # 平均气温
# 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# 一次性传入多组数据(x相同可省略重复x)
lines =plt.plot(
days, temp_high, 'ro-', # 红色(r)、圆点(o)、实线(-)
days, temp_low, 'gs--', # 绿色(g)、正方形(s)、虚线(--)
days, temp_avg, 'b^-.', # 蓝色(b)、三角形(^)、点划线(-.)
)
# 添加图表元素
plt.title('某城市一周气温变化(最高/最低/平均)', fontsize=15, pad=20)
plt.xlabel('星期', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('气温(℃)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylim(10, 30) # 调整y轴范围
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
# 手动设置图例标签
plt.legend(
handles=lines, # 使用plot返回的线条对象
labels=['最高气温', '最低气温', '平均气温'], # 手动指定标签
loc='best', # 位置自动
fontsize=11, # 字体大小
frameon=True, # 显示边框
fancybox=True, # 圆角边框
shadow=True, # 阴影效果
)
# 美化边框
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
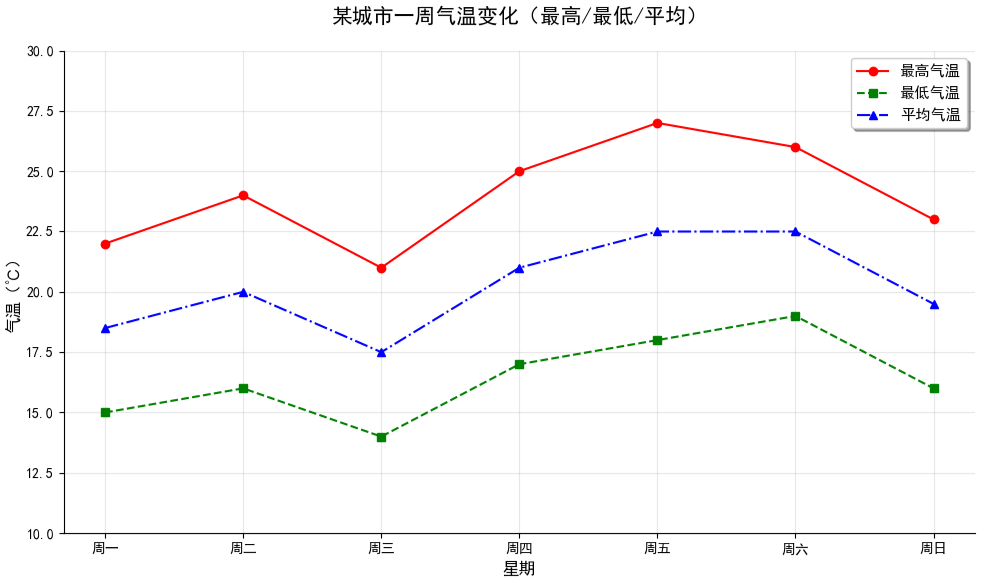
更多内容可以前往官网查看:
https://matplotlib.org/stable/


本篇文章来源于微信公众号: 码农设计师
